How to Differentiate a Data Hub, a Data Lake, and a Data Warehouse |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › master data management data warehouse › How to Differentiate a Data Hub, a Data Lake, and a Data Warehouse |
How to Differentiate a Data Hub, a Data Lake, and a Data Warehouse

Data Hubs are getting more attention as many enterprises are looking at the different solutions in the market to build their own, in order to handle their core critical enterprise data. However, this technology is still sometimes seen as an interchangeable alternative to Data Warehouses or Data Lakes. [Learn more about the difference between a Data Hub, a Data Lake and a Data Warehouse in French.] 
According to Gartner, “client inquiries referring to data hubs increased by 20% from 2018 through 2019.” Interestingly, the analyst firm noticed that “more than 25% of these inquiries were actually about data lake concepts(1).” Have you ever been in a situation where you wonder whether you need to implement a data warehouse, a data lake or a data hub? Probably. There is still a lot of confusion when it comes to differentiating these three concepts as they sound similar. In reality, they have important differences that everyone should be aware of. To clear up confusion around these concepts, here are some definitions and purposes of each: The Data WarehouseThe Data Warehouse is a central repository of integrated and structured data from two or more disparate sources. This system is mainly used for reporting and data analysis, and is considered a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses implement predefined and repeatable analytics patterns distributed to a large number of users in the enterprise. The Data LakeThe Data Lake is a single store of all structured and unstructured enterprise data. It hosts unrefined data with limited quality assurance and requires the consumer to process and manually add value to the data. Data Lakes are, in general, a good foundation for data preparation, reporting, visualization, advanced analytics, data science and machine learning. The Data HubThe Data Hub is the go-to place for the core data within an enterprise, and according to a recent Semarchy article, the future of data management. It centralizes the enterprise’s data that is critical across applications, and it enables seamless data sharing between diverse endpoints, while being the main source of trusted data for the data governance initiative. Data hubs provide master data to enterprise applications and processes. They are also used to connect business applications to analytics structures such as data warehouses and data lakes. 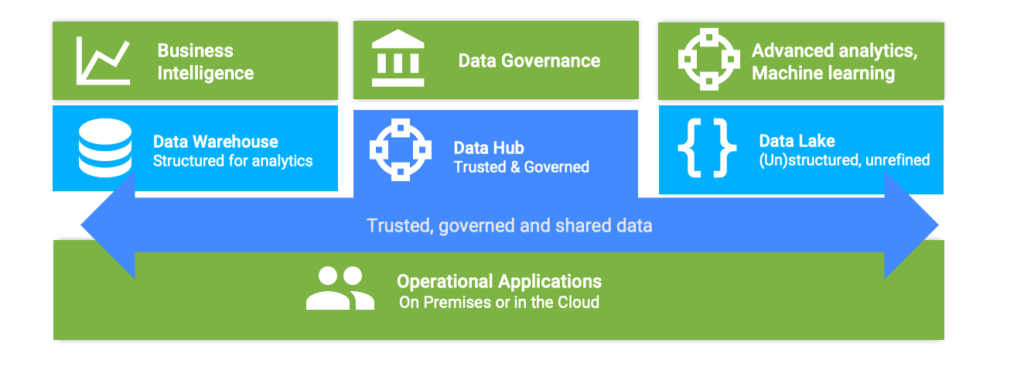 They all look similar but they are different
They all look similar but they are different
In short, data warehouses and data lakes are endpoints for data collection that exist to support the analytics of an enterprise, while data hubs serve as points of mediation and data sharing. They are not focused solely on analytical uses of data. In some cases, data warehouses and data lakes offer governance controls, but only in a reactive manner, whereas data hubs proactively apply governance to the data flowing across the infrastructure. Data warehouses, data lakes, and data hubs are not interchangeable alternatives. Nevertheless, they are complementary, and together they can support data-driven initiatives and digital transformation. The table below summarizes their similarities and differences: Data HubData WarehouseData LakePrimary UsageOperational ProcessesAnalytics and reportingAnalytics, reporting and Machine LearningData ShapeStructuredStructuredStructured & UnstructuredData GovernanceMain pillar for all data governance enforcement rulesAfter-the fact governance as it consumes existing operational data“Use at your own risk” data approach. Lightly governed.Data QualityVery high qualityHigh qualityMedium / low qualityIntegration with Enterprise AppsBi-directional real-time integration with existing business processes via APIs.Mono-directional ETL or ELT in batch mode. Transformed and cleansed data is refreshed at low frequency (hourly, daily or weekly)Mono-directional ETL or ELT in batch mode. Data is dumped without control into the lake assuming future cleansing by the consumer.Business Users InteractionsCan be the primary source of authoring of key data elements such as master data and reference data. Exposes user-friendly interfaces for data authoring, data stewardship and search.Offers a read-only access to aggregated and reconciled data through reports, analytic dashboards or ad-hoc queries.Requires data cleansing / preparation before consumption. Access to business users is mainly offered via reports, dashboards or ad-hoc queries. Used to stage Machine Learning data sets.Enterprise Operational ProcessesPrimary repository for reliable data exposed in business processes. Can be the primary conductor of enterprise business processes.Mainly serves analytics processes.Mainly serves Machine Learning processes.Are you looking for a data management solution for your business? Semarchy’s Unified Data Platform, featuring our revolutionary xDM and xDI solutions, is the all-in-one low-to-no-code solution for data management, governance, and integration. Click here to request a custom demo tailored to your business needs. Read more about the implementation of better, faster, and more accurate data with our free eBook, Riding the Real-Time Wave: Data Strategies & Enabling Technologies. Learn More(1) Gartner Article ID G00465401: Data Hubs, Data Lakes and Data Warehouses: How They Are Different and Why They Are Better Together. Published 13 February 2020 – By Analysts Ted Friedman and Nick Heudecker — Requires a Gartner account. |
【本文地址】